🌿 Introduction
Living off the grid has become more than a trend—it’s a lifestyle shift toward independence, resilience, and sustainability. When people imagine off-grid living, they often think of solar power, gardens, or tiny homes… but the real foundation of self-reliance is water. Understanding the 8 off grid water systems that actually work in different climates, budgets, and property types is crucial for anyone who wants long-term, reliable access to clean water.
If you’re ready to build a self-sufficient homestead, the resource-rich guide The Self-Sufficient Backyard offers practical blueprints for water harvesting, storage, and filtration—making it a valuable companion for any off-grid setup.
In this guide, we’re breaking down the most dependable 8 off grid water systems, showing you how each works, their pros and cons, and the best situations for using them. Whether you’re collecting rainwater, tapping into a natural spring, pumping from a creek, or generating water from air, this comprehensive breakdown will help you choose the right system for long-term reliability.
You’ll also find real-world examples, power options, filtration advice, and crucial tips for staying compliant with local water laws. Ready to master your water supply? Let’s dive into the systems that keep off-grid homes running, no matter what the world throws your way.
🌧️ Rainwater Harvesting Systems (System #1)
Rainwater harvesting is one of the oldest and most reliable 8 off grid water systems, and for many homesteaders it becomes the primary year-round water source. This system collects rain from rooftops or catchment surfaces and stores it in tanks, barrels, or underground cisterns. Because rainwater is naturally soft, clean, and neutral in pH, it’s ideal for drinking, gardening, livestock, and household use once properly filtered.
A well-built rainwater setup becomes even more powerful when combined with modern off-grid tools like the AquaTower, which automates filtering and distribution. This makes rainwater systems not only efficient but also fully self-sustaining—perfect for remote properties or cabins.
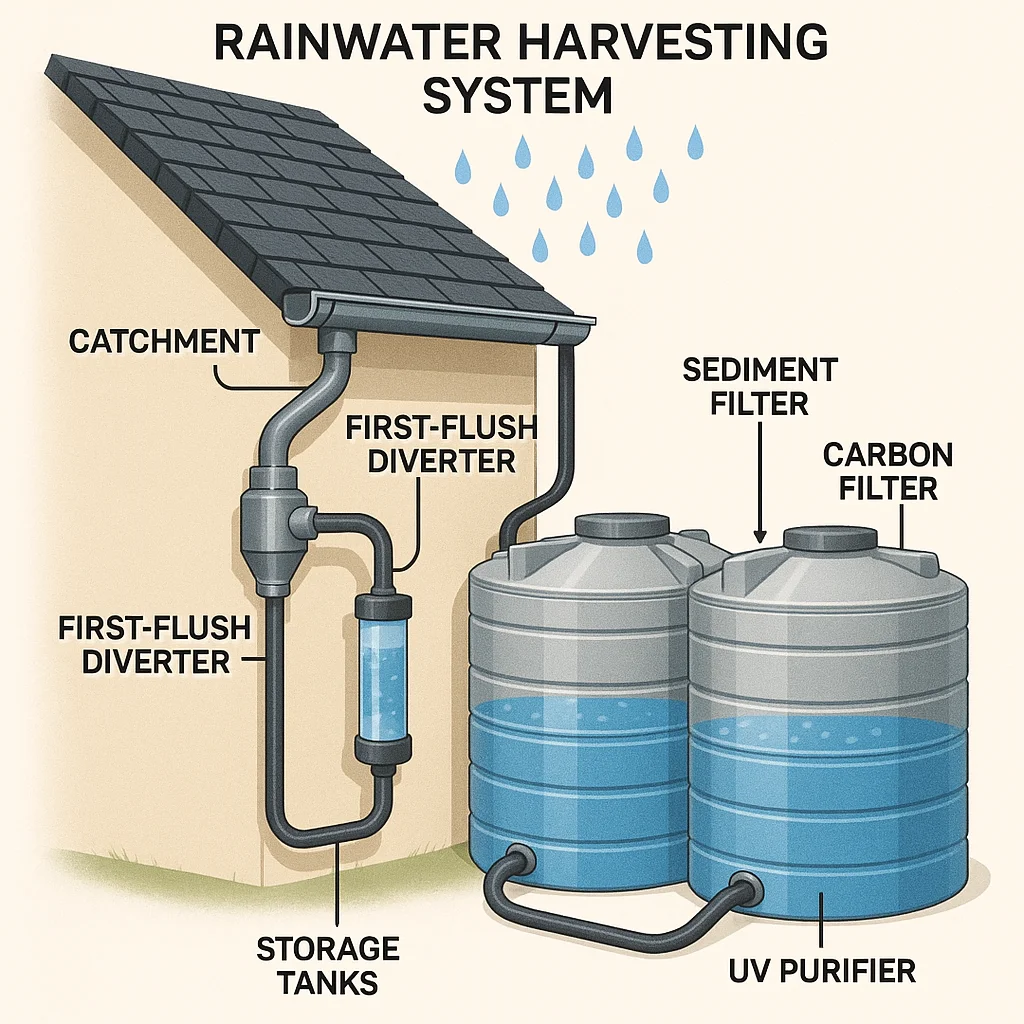
Rainwater systems usually consist of three core components:
-
Catchment surface – Most commonly a roof, but it can also be a tarp system or metal sheet.
-
Guttering and first-flush diverters – Removes debris, leaves, pollen, and contaminants.
-
Storage + filtration – Tanks (plastic, metal, concrete), sediment filters, carbon filters, and UV systems.
Gravity-Fed vs. Pump-Based Rainwater Systems
-
Gravity-fed systems use elevation: tanks positioned higher than the home supply water pressure without electricity.
-
Pump-based systems provide consistent pressure for showers, appliances, and irrigation. These can run on solar power or a backup generator like the Ultimate OFF-GRID Generator, which ensures reliable performance during cloudy seasons.
Best Uses for Rainwater Systems
Rainwater is especially excellent in the following situations:
-
Areas with consistent rainfall
-
High-roof homes or barns offering large collection area
-
Homesteads needing potable water with minimal energy input
-
Garden-heavy properties needing irrigation without draining wells
Rainwater harvesting is legal in most regions, though some states require diverters or permits. It’s one of the simplest ways to build long-term resilience and reduce dependence on unpredictable municipal systems.
💧 Groundwater Wells (System #2)
A properly installed well is one of the strongest long-term solutions among the 8 off grid water systems, offering a dependable supply of groundwater that can last decades with minimal maintenance. Wells are especially valuable for homesteaders who live in areas with unpredictable rainfall or who require a year-round, high-volume water source.
Wells come in two main types:
🥾 Shallow Wells
Shallow wells reach groundwater close to the surface—typically less than 50 feet deep.
Pros:
-
Cheaper to install
-
Can sometimes be hand-dug
-
Perfect for small cabins or seasonal use
Cons:
-
More vulnerable to contamination
-
Lower output during drought
⛏️ Deep Wells
Deep wells penetrate hundreds of feet into the aquifer.
Pros:
-
Extremely clean water
-
Consistent water pressure
-
Unaffected by surface runoff or drought
Cons:
-
More expensive to drill
-
Requires stronger pumps
Off-Grid Pump Options
Because wells require energy to draw water, off-grid power systems become essential. The three most reliable choices are:
1. Solar Pumps
Powered by a dedicated panel array, solar pumps are the most common off-grid pumping system. They provide steady pressure, run silently, and require almost no maintenance.
2. Hand Pumps
Hand pumps are excellent backups during outages. They can draw water even from deep wells when sized correctly.
3. Generator-Powered Pumps
When deep well pumps require more wattage than solar alone can supply, a backup generator becomes essential. A compact, high-output unit like the Ultimate OFF-GRID Generator ensures year-round pumping power—even during long periods without sun.
Well Water Quality & Filtration
Although groundwater is often cleaner than surface water, it may contain minerals, iron, sulfur, or bacteria.
Most homesteaders install:
-
Sediment filters
-
Activated carbon filters
-
UV purification
-
Iron removal systems (if needed)
Wells remain one of the most scalable and reliable water solutions for larger off-grid properties, small farms, and long-term homesteads.
⛰️ Natural Spring Water Systems (System #3)
Among the 8 off grid water systems, a natural spring is one of the purest and most sustainable sources you can possibly have. Springs deliver groundwater that naturally flows to the surface through cracks, fissures, or permeable layers in the earth. Because this water is already filtered through sediment and stone, many springs have exceptionally high clarity and mineral balance.
If your property has a naturally occurring spring—or even signs of seepage—this can become a lifelong water supply with minimal mechanical intervention.
How to Locate and Assess a Natural Spring
Springs are more common in mountainous, forested, or sloped regions. Key indicators include:
-
Constant wet patches or mossy areas
-
Water trickling from rock outcrops
-
Seasonal seepage after rains
-
Cooling temperature near ground flow points
Professional testing is crucial. Even though spring water is often clean, it may still contain bacteria or runoff contaminants depending on soil composition and wildlife activity.
Building a Spring Box
A spring box is the foundation of a reliable spring-based system. It protects the water source from contamination and channels flow into a controlled supply line.
A good spring box includes:
-
A sealed concrete or plastic enclosure to prevent debris
-
A gravel pre-filter bed
-
Overflow piping for high-flow seasons
-
A distribution line feeding tanks or home plumbing
-
A secondary filtration system (UV, ceramic, or carbon)
Once stabilized, spring systems can provide consistent year-round flow with virtually zero energy cost.
Gravity-Fed Advantages
One of the greatest strengths of spring-fed systems is natural elevation. Many springs emerge uphill from living areas, allowing you to build a gravity-fed water system that delivers pressure without pumps or electricity.
This saves thousands in hardware and eliminates dependence on power sources entirely—making spring-fed setups one of the most resilient off grid water systems.
Enhancing Spring Water Reliability
Even with gravity flow, some homesteaders add:
-
A backup storage tank
-
UV filtration
-
A pump-powered pressure system for showers or appliances
For remote properties, pairing your system with a survival-focused resource like The Self-Sufficient Backyard gives additional guidance on seasonal water protection, piping techniques, winter-proofing, and long-term spring management.
🏞️ River, Stream & Creek Pumping Systems (System #4)
Surface water sources—such as rivers, streams, creeks, and even seasonal runoffs—are extremely valuable among the 8 off grid water systems, especially for properties blessed with natural flowing water. These systems can provide high-volume water for irrigation, livestock, cleaning, and with proper filtration, even safe drinking water.
Surface water is abundant and renewable, but it also demands responsible management, filtering, and in many regions, an understanding of water rights.
Understanding Water Rights & Permits
Before tapping into a stream or creek, it’s important to verify local laws.
Regulations vary by region and may involve:
-
Riparian water rights
-
Permit requirements
-
Limits on water diversion
-
Environmental impact considerations
While most homesteaders can legally use small volumes of water for personal or agricultural purposes, large-scale pumping may require authorization.
Low-Energy Off-Grid Pumping Options
Pumping water from a stream doesn’t have to be power-intensive. Many homesteads rely on clever low-energy or zero-energy solutions, including:
🌬️ 1. Ram Pumps
Ram pumps use the natural force of flowing water to pump a portion uphill—no electricity required. They are perfect for steep terrain with consistent flow.
☀️ 2. Solar-Powered Pumps
A solar pump combined with a small battery bank can deliver pressurized water on-demand. This is ideal for year-round use with minimal maintenance.
🔋 3. Generator-Assisted Pumps
When you need strong pumping force, especially for long distances or steep elevation, a reliable generator can make the difference. A unit like the Ultimate OFF-GRID Generator ensures steady, high-output pumping even during periods of low sunlight or heavy use.
Filtration & Purification for Surface Water
Surface water is the most vulnerable to contamination due to:
-
Wildlife
-
Agricultural runoff
-
Sediment
-
Seasonal debris
Essential filtration stages include:
-
Sediment filter (removes dirt, sand, silt)
-
Carbon filter (removes chemicals, odors, VOCs)
-
UV sterilization (kills bacteria, viruses, protozoa)
-
Optional ceramic filter (long-term, off-grid friendly)
Systems like the AquaTower work exceptionally well here due to their multi-layer filtering design and off-grid compatibility.
Pumping System Best Uses
Surface water systems excel in properties where you have:
-
A flowing creek on-site
-
Sufficient elevation change for ram pumps
-
Solar exposure for solar pump arrays
-
The need to irrigate gardens, orchards, or livestock pastures
With the right filtration setup, they can even support full household water supply.
☁️ Atmospheric Water Generators (System #5)
Among the 8 off grid water systems, atmospheric water generators (AWGs) are the most technologically advanced. They don’t rely on rainfall, wells, or surface water—instead, they extract clean, drinkable water directly from the moisture in the air. This makes AWGs a powerful solution for homesteaders living in regions with unreliable rainfall or limited groundwater.
Even in semi-arid or variable climates, a properly sized atmospheric system can provide anywhere from 2 to 20 gallons of purified water per day, depending on humidity levels and unit capacity.
How Atmospheric Water Generators Work
AWGs condense water vapor by cooling air below the dew point. The resulting liquid is then filtered and purified. Most AWGs include:
-
Air intake system
-
Cooling and condensation coils
-
Sediment + carbon filtration
-
UV purification
-
Internal storage tank
This means the water produced is typically cleaner than municipal tap water, free from heavy metals, runoff, or microbiological contamination.
Ideal Climates for AWGs
AWGs perform best in environments with:
-
60%+ humidity
-
Temperatures above 70°F (21°C)
-
Moderate to high airflow
However, even drier climates can generate meaningful amounts of water with larger coil systems or hybrid solar-powered models.
Off-Grid Powering Options
One challenge with AWGs is that they require electricity to operate. Fortunately, off-grid homes can run AWGs efficiently with:
☀️ Solar Power Systems
Pairing AWGs with solar panels is the most common solution. A dedicated solar array ensures your system runs during peak heat—perfect for maximizing water production.
🔋 Battery Banks
A battery bank stores excess solar power generated during the day, allowing the AWG to run overnight when humidity tends to rise naturally.
⚡ Backup Generator
During extended cloudy weather or high water demand periods, a generator such as the Ultimate OFF-GRID Generator ensures continuous production.
Maintenance & Care
AWGs require relatively low maintenance:
-
Replace filters every 3–6 months
-
Clean the coils to maintain condensation efficiency
-
Keep airflow unobstructed
-
Drain and sanitize the internal tank periodically
Unlike wells or surface systems, there’s no risk of drought-driven depletion—making AWGs a noteworthy asset in a diversified off-grid water plan.
Why AWGs Are a Top Choice for Modern Homesteads
Modern preppers and off-grid homeowners appreciate AWGs because they deliver clean water independent of geography. Even if your land has no creek, no spring, and no well potential, atmospheric water generation gives you a reliable alternative source.
For a balanced off-grid setup, pairing an AWG with a step-by-step homestead planner like The Self-Sufficient Backyard helps you integrate atmospheric water efficiently with other systems, storage, and filtration.
🔆 Solar-Powered Water Pumping Systems (System #6)
Solar-powered pumping has become one of the most popular choices within the 8 off grid water systems, thanks to its reliability, low maintenance requirements, and ability to operate without fuel or grid power. Whether you’re pulling water from a well, a rainwater tank, a creek, or even an underground cistern, solar pumps provide a consistent and renewable way to move water around your property.
Solar water pumping is especially valuable in remote homesteads where running electrical lines would be expensive—or simply impossible.
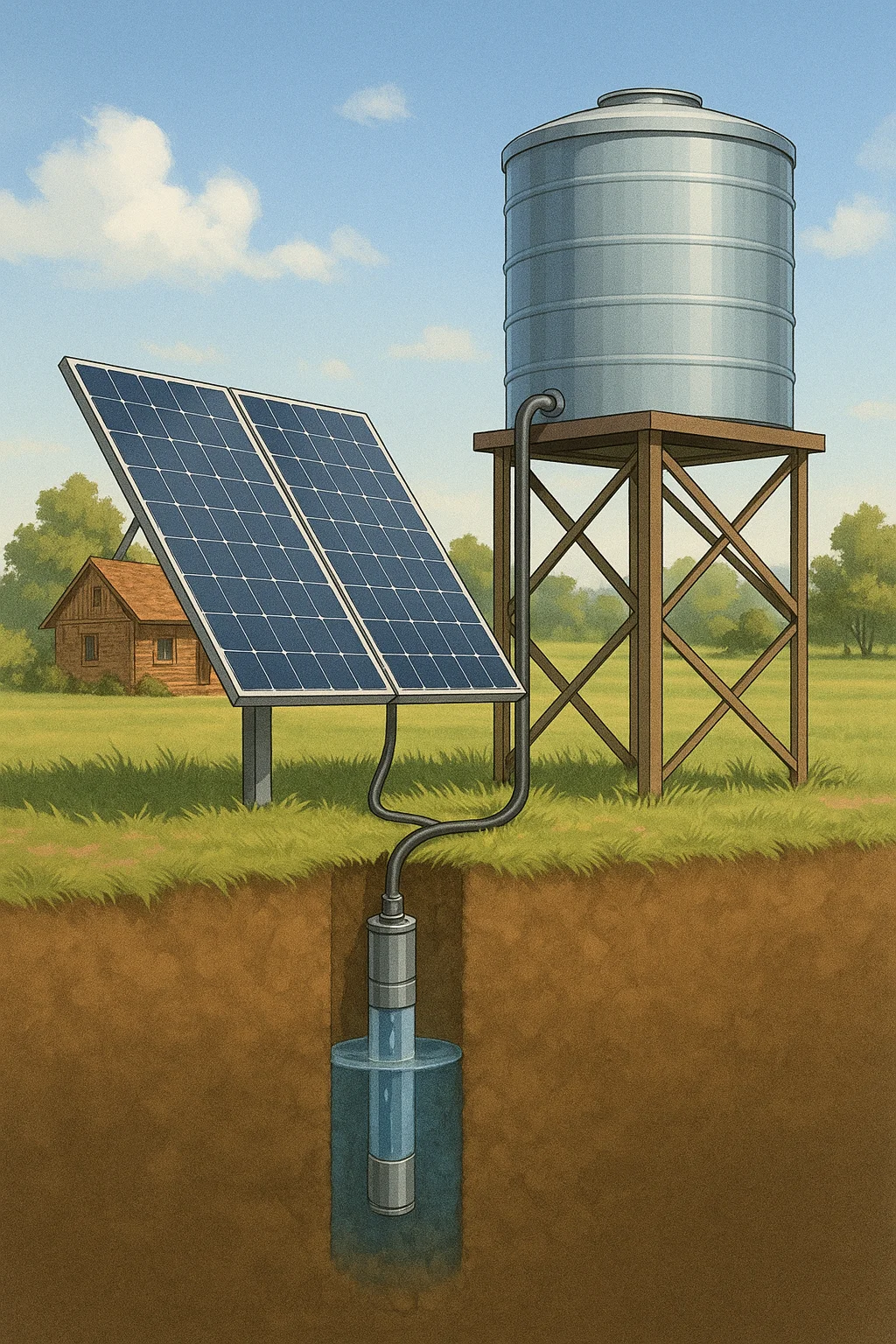

How Solar Pump Systems Work
A complete solar water pump system usually includes:
-
Solar panels dedicated to powering the pump
-
Pump controller to regulate flow and prevent damage
-
Submersible or surface pump depending on source
-
Optional battery backup for nighttime or cloudy days
-
Storage tank or pressure tank for consistent output
The panels supply DC power directly to the pump, which then transports water to a tank, home plumbing system, or field irrigation system.
Types of Solar Pumps
1. Submersible Solar Pumps
Designed for deep wells, cisterns, or underground tanks.
Best for:
-
Wells 50–400 feet deep
-
Whole-house water supply
-
Livestock watering systems
2. Surface Solar Pumps
Used for shallow water sources like streams, ponds, rain tanks, or springs.
Best for:
-
Irrigation
-
Garden watering
-
Filling elevated tanks
3. Hybrid Solar Pumps
These can switch between solar, battery, or generator power as needed—making them extremely useful for unpredictable climates.
Why Solar Pumps Excel Off-Grid
Solar pumping systems shine in off-grid settings because they:
-
Require no fuel
-
Operate silently
-
Have very low maintenance
-
Are ideal for remote or mountainous terrain
-
Work well with gravity-fed tank setups
-
Integrate easily with filtration systems like the AquaTower
Plus, solar pumps are far more efficient today than a decade ago, allowing even small systems to meet full household demands.
When sunlight is unreliable for extended periods, many homesteaders keep a backup generator—such as the Ultimate OFF-GRID Generator—to maintain water flow during emergencies.
Best Use Cases for Solar Pump Systems
Solar pumping is ideal for:
-
Deep well systems with no access to grid power
-
Rainwater tanks needing pressurized delivery
-
Orchards, gardens, greenhouses, or livestock paddocks
-
Off-grid cabins or tiny homes
-
Backup systems for drought-prone areas
Solar pumps are also extremely scalable. You can run a single pump for basic household use—or build a full multi-zone irrigation system for large acreage.
Integrating Solar Pumps with Water Storage
Most off-grid homes pair solar pumps with:
-
1,500–5,000 gallon above-ground tanks
-
Buried cisterns to protect water during winter
-
Pressure tanks for indoor plumbing stability
If you prefer a more structured planning approach, guides like The Self-Sufficient Backyard outline sample pump-and-tank configurations designed for long-term resilience.
🛢️ Off-Grid Water Storage Solutions (System #7)
Water storage is the backbone of all 8 off grid water systems, because no matter how you collect or generate water—rainwater, well water, spring water, creek water, or atmospheric water—you must be able to store it safely and reliably. Proper storage ensures that you have enough water during droughts, winter freezes, power outages, or seasonal fluctuations.
A well-designed storage system also protects your water from contamination, algae growth, and temperature swings, making it absolutely essential for long-term off-grid living.
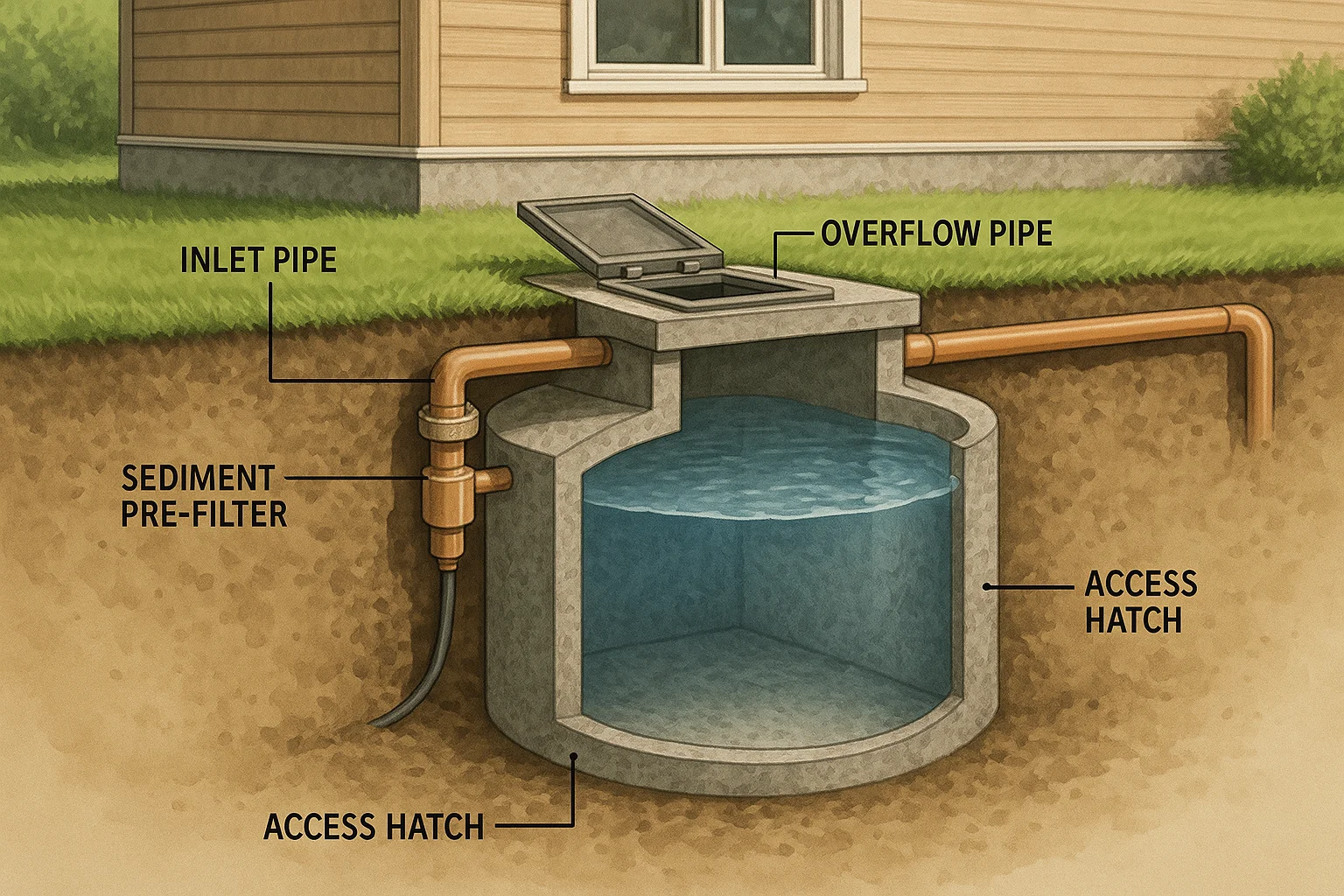
Types of Off-Grid Water Storage Tanks
Different homesteads require different storage solutions depending on climate, space, and water source.
1. Above-Ground Poly Tanks
These are the most common tank type, used by thousands of off-grid homeowners.
Pros:
-
Affordable
-
Easy to install
-
UV-resistant
-
Available in sizes from 50 to 10,000 gallons
Cons:
-
Vulnerable to freezing in winter climates
-
More visible above ground
2. Underground Cisterns
Designed for long-term stability, excellent protection from the elements, and temperature regulation.
Pros:
-
Hidden and aesthetically clean
-
Freeze-proof
-
Great for large capacities
-
Long lifespan
Cons:
-
Higher installation cost
-
Requires excavation
-
Harder to access for maintenance
3. Metal or Concrete Tanks
These tanks last decades and are ideal for large homesteads.
Pros:
-
Extremely durable
-
Fire-resistant
-
Available in very large sizes (20,000+ gallons)
Cons:
-
Heavier
-
More expensive
-
Requires careful sealing to prevent leaks
How Long Will a 5,000-Gallon Tank Last?
This is one of the most common questions for off-grid living, and the answer depends on daily usage.
Average off-grid household water use:
-
Indoor use: 40–60 gallons per person/day
-
Outdoor use: Variable
For a 2-person household using 50 gallons/day each:
100 gallons/day → 5,000 gallons lasts ~50 days
For a conservative household using 30 gallons/day each:
60 gallons/day → 5,000 gallons lasts ~83 days
For survival-level use (10–15 gallons/day each):
20–30 gallons/day → 5,000 gallons lasts 166–250 days
This makes large storage tanks invaluable for drought seasons, remote properties, or intermittent water sources.
Protecting Stored Water
To keep stored water safe and potable, off-grid homes use:
-
Sediment pre-filters
-
Carbon filtration
-
UV sterilizers
-
Opaque tanks (blocks sunlight, prevents algae)
-
First-flush diverters (for rainwater)
-
Tank screens (keeps insects and debris out)
Filtration systems like the AquaTower integrate perfectly with storage tanks, ensuring that every gallon entering the home is clean and safe.
Insulation and Freeze Protection
Winter climates can freeze tanks and destroy pipes if not managed well.
Solutions include:
-
Burying tanks underground
-
Wrapping pipes in heat tape
-
Using insulated tank jackets
-
Positioning tanks inside greenhouses or sheds
-
Keeping tanks at least ⅓ full at all times
Powering Your Tank System
Most off-grid water storage setups use gravity, but pumps are sometimes required. During low sunlight periods or emergencies, a backup generator such as the Ultimate OFF-GRID Generator ensures you can always move water when needed.
For detailed tank layouts and seasonal strategies, guides like The Self-Sufficient Backyard offer diagrams and homestead-tested storage plans.
🧪 Filtration & Purification Systems (System #8)
Even if you collect, store, or pump huge amounts of water, it’s not truly safe until you filter and purify it. This makes filtration the most critical component of all 8 off grid water systems. Whether your water comes from a well, rainwater tank, spring, or creek, you must remove sediment, chemicals, and microorganisms to ensure potable quality.
A reliable 8 off grid water systems water filtration setup protects your family from bacteria, viruses, protozoa, heavy metals, agricultural runoff, and environmental contaminants — many of which can be invisible but extremely harmful.
The 5 Core Stages of Off-Grid Water Filtration
Most off-grid homeowners use a multi-stage approach. Each stage removes specific types of impurities.
1. Sediment Filtration (First Stage)
Removes:
-
Dirt
-
Sand
-
Rust
-
Silt
-
Debris
This protects later filters and extends their lifespan.
2. Activated Carbon Filtration
Removes:
-
Chemicals
-
Chlorine
-
Pesticides
-
VOCs
-
Odors and taste issues
Carbon filters are essential for surface water and rainwater systems.
3. Ceramic Filtration
Perfect for long-term off-grid setups because ceramic filters:
-
Are cleanable and reusable
-
Last years
-
Remove bacteria, cysts, and protozoa
They are extremely reliable in wilderness or survival scenarios.
4. Reverse Osmosis (Optional)
Reverse osmosis removes nearly everything, including:
-
Fluoride
-
Heavy metals
-
Dissolved minerals
-
Salt (from brackish water)
The downside: RO systems require pressure or electricity, making them less ideal unless paired with a generator or solar power.
5. UV Purification (Final Stage)
UV systems kill:
-
Bacteria
-
Viruses
-
Protozoa
-
Pathogens
They consume very little power and are considered the gold standard for final sterilization.
Off-Grid-Friendly Filtration Solutions
For homesteaders who want a dependable, plug-and-play option, the AquaTower is an excellent choice. It combines multiple filtration layers with gravity or low-power operation, making it ideal for cabins, retreats, and remote homes.
For whole-house protection, many homeowners combine:
-
Sediment + carbon filter at the tank or well
-
UV purifier inside the home
-
Ceramic countertop filter for drinking water
This creates a resilient, multi-layer water purification strategy.
Emergency Water Purification
In emergencies or during system failures, simple purification methods become invaluable:
-
Boiling (kills all microorganisms)
-
Solar disinfection (SODIS)
-
Chlorine drops
-
Portable gravity filters
-
Ceramic survival filters
These backup methods ensure you always have safe water no matter the situation.
For broader preparedness coverage, tools like The Lost Superfoods teach additional survival strategies for water, food storage, and emergency resilience.
Why Filtration Is the Most Important System
Even the cleanest source—such as a spring or deep well—can change over time. Seasonal shifts, wildlife contamination, and sediment infiltration can turn previously safe water unsafe. A solid filtration system ensures that every gallon you drink is consistent, dependable, and fully potable.
Among the 8 off grid water systems, filtration ties everything together. It is the final—and arguably most essential—step in making water safe for long-term consumption.
🧭 Choosing the Best Off-Grid Water System for Your Property
Now that we’ve covered all 8 off grid water systems, the next step is understanding which combination works best for YOUR property. Every homestead is unique — climate, terrain, water rights, rainfall, soil type, and energy availability all play major roles in determining the right system.
The most resilient off-grid setups use 2–3 water systems working together, ensuring redundancy, year-round supply, and protection against droughts, equipment failures, or seasonal changes.
1. Climate-Based Recommendations
Different climates favor different water systems.
🏜️ Arid or Semi-Arid Regions
Best systems:
-
Atmospheric Water Generator (AWG)
-
Deep well
-
Large water storage (5,000–20,000 gallons)
-
Solar pump system
Rainwater is less reliable, so production-based systems become more important.
🌧️ High-Rainfall Regions
Best systems:
-
Rainwater harvesting (primary)
-
Spring water (if available)
-
Creek or stream pumping
-
Medium-sized storage
Filtration remains crucial because surface water changes with seasons.
🌲 Mountain or Forested Areas
Best systems:
-
Gravity-fed spring system
-
Stream or creek pumping
-
Above-ground or underground cisterns
These systems require minimal electricity and offer year-round flow.
🌾 Flat Farmland or Rural Plains
Best systems:
-
Deep well with solar pump
-
Rainwater harvesting for garden/livestock
-
Backup storage tanks
Wells often provide the most consistent water source in these areas.
2. Property Topography
Slope and elevation determine whether gravity flow is possible.
Sloped land:
Gravity-fed spring or rainwater systems are ideal.
Flat land:
You may need solar or generator-powered pumps.
Steep terrain:
Ram pumps, gravity-flow tanks, and elevated catchment systems work exceptionally well.
3. Budget Considerations
The cost of off-grid water systems varies widely.
Low-Budget Options ($0–$500)
-
Basic rainwater harvesting
-
Manual filtration (ceramic/carbon)
-
Gravity-fed systems
-
Small storage tanks
Mid-Budget Options ($500–$3,500)
-
Solar pump systems
-
Ram pump setups
-
Medium cisterns
-
Whole-house filters
High-Budget Options ($5,000–$20,000+)
-
Deep well installation
-
Large underground cisterns
-
Full off-grid filtration + UV
-
Atmospheric Water Generator (high-capacity)
For structured planning and budget-friendly alternatives, guides like The Self-Sufficient Backyard provide step-by-step, cost-saving projects that cut expenses dramatically.
4. Recommended System Combinations
The strongest off-grid water strategies combine redundancy with diversity:
Combination A: The “Zero-Fail” System
-
Deep well
-
Solar pump
-
5,000–10,000 gallon storage
-
Multi-stage filtration (sediment + carbon + UV)
Combination B: The “Homestead Rain Master”
-
Rainwater harvesting
-
Large cistern (5,000–20,000 gallons)
-
Gravity-fed backup system
-
AquaTower filtration
Combination C: The “Off-Grid Pioneer”
-
Spring-fed gravity system
-
Backup rainwater
-
Ceramic + carbon filter stack
-
Minimal electricity required
Combination D: The “Arid Climate Survivalist”
-
AWG system
-
Deep well (if available)
-
Heavy storage
-
Generator backup for pumping
5. Backup Power for Water Systems
Even the most efficient water systems benefit from backup power.
A generator like the Ultimate OFF-GRID Generator ensures:
-
Pumps run during low sunlight
-
Filtration stays operational
-
Emergencies don’t disrupt water supply
This is one of the biggest upgrades to overall water resilience.
6. Food + Water Integration
Water systems often pair with food resilience. Resources like The Lost Superfoods help you build complete emergency readiness around your water system—especially important for remote homesteads.
Final Recommendation
No single system is perfect. The best approach is to choose at least two primary water sources plus filtration and storage. This ensures your homestead remains functional year-round, even during droughts, storms, or grid failures.
Among all 8 off grid water systems, filtration and storage remain non-negotiable pillars of safety and resilience.
🏁 Conclusion: Building a Resilient Off-Grid Water System
Mastering the 8 off grid water systems is one of the most important steps in creating a secure, resilient, and fully independent homestead. Water is the foundation of off-grid life — without a dependable source, everything else becomes unstable. Whether you rely on rainfall, wells, springs, streams, atmospheric generation, solar pumps, or heavy-duty storage, the true strength of your water plan lies in redundancy, diversity, and proper filtration.
Each of the eight systems excels in different environments. Wells deliver year-round reliability, rainwater harvesting provides sustainable collection, springs offer gravity-fed simplicity, streams supply high-volume water, AWGs create water from thin air, and filtration ensures every drop is safe to drink. When combined strategically, they form a powerhouse water network capable of supporting families, livestock, gardens, and emergency needs — even in long-term grid-down scenarios.
Most successful homesteaders use two or three complimentary systems, backed by filtration and large storage tanks. This guarantees water flow even during droughts, storms, seasonal drops, or mechanical failures. Whether you live in a high-rainfall region, a dry climate, a remote mountainous area, or a rural plain, there is a combination of systems that will work perfectly for your land.
For step-by-step instructions, layout diagrams, and cost-saving off-grid water hacks, resources like The Self-Sufficient Backyard help you build reliable systems without overspending. And for complete emergency protection, pairing your water strategy with preparedness tools like The Lost Superfoods creates a truly self-sufficient lifestyle.
The more you diversify your water systems, the more secure your off-grid life becomes. With proper planning, any property can achieve sustainable, long-term water independence — no matter the climate, terrain, or remoteness.
You now have the full blueprint for choosing, installing, and maintaining the best 8 off grid water systems for your homestead. Your journey toward total self-reliance starts with your water supply — and you’re now prepared to build it right.
❓ FAQ Section
Below are the fully expanded answers to your provided FAQs, each optimized for SEO and aligned with the theme of 8 off grid water systems. These FAQs will appear at the end of your full article.
❓ How do you get water if you live off-grid?
Living off-grid means you must source your own water instead of relying on municipal supply. Most homesteaders use a combination of the 8 off grid water systems, which include:
-
Rainwater harvesting
-
Deep or shallow wells
-
Natural spring systems
-
Creek or river pumping
-
Atmospheric Water Generators (AWGs)
-
Solar-powered pumping systems
-
Large water storage tanks or cisterns
-
Multi-stage filtration and purification
A common strategy is to combine at least two water sources (for example, a well + rainwater + storage) to ensure reliability year-round. Filtration and purification are also essential to keep all water potable and safe.
❓ Why is living off-grid illegal?
Living off-grid is not illegal, but certain components of off-grid living can be regulated. The confusion often comes from:
-
Local building codes
-
Zoning restrictions
-
Sewage and septic requirements
-
Water rights laws
-
Electrical or safety standards
Some counties require minimum house sizes, septic inspections, well permits, and registered addresses for emergency services. Off-grid water systems like rainwater or creek pumping may also require adherence to local water rights.
The key is to research local laws before building. Many rural areas fully support off-grid living; others require specific permits. The systems themselves—such as the 8 off grid water systems—are fully legal when installed correctly.
❓ How long will a 5,000-gallon water tank last?
The lifespan of a 5,000-gallon tank depends entirely on household water usage.
Typical Usage Patterns
| Household Type | Daily Use | 5,000 Gallons Lasts |
|---|---|---|
| 2-person homestead (moderate use) | ~100 gallons/day | ~50 days |
| 2-person conservative home | ~60 gallons/day | ~83 days |
| Survival/rationing level | 20–30 gallons/day | 166–250 days |
| Family of 4 (moderate use) | 150–200 gallons/day | 25–33 days |
Factors that influence lifespan include:
-
Laundry frequency
-
Dishwashing methods
-
Garden or livestock watering
-
Shower length
-
Climate and season
For most off-grid homes, 5,000 gallons is considered a strong mid-range storage capacity—especially when paired with a well, rainwater system, or spring.
❓ What is the best way to pump water off the grid?
The best pumping method depends on your water source and available energy. Among the 8 off grid water systems, these are the top pumping solutions:
1. Solar-Powered Water Pumps
Best all-around option. Works for wells, tanks, springs, and creeks.
Low maintenance, highly reliable, no fuel required.
2. Gravity-Fed Systems
If your water source is elevated (spring, hill tank, etc.), gravity gives you free water pressure with zero electricity.
3. Ram Pumps
Use moving water (streams/creeks) to push a percentage of water uphill without power.
4. Manual/Hand Pumps
Excellent for emergency backups or deep-well redundancy.
5. Generator-Powered Pumps
Ideal when you need strong, consistent pumping—especially for deep wells.
A backup like the Ultimate OFF-GRID Generator ensures reliability during long cloudy periods or heavy usage.
In most homesteads, a solar pump + gravity-fed backup is the perfect combo for long-term off-grid resilience.